Navigating regulatory compliance is a significant hurdle that modern manufacturers must overcome to preserve their competitive advantage. According to The International Centre for Industrial Transformation (INCIT), “by adhering to regulations and standards, you ensure product safety, quality, and ethical practices, which are essential for maintaining consumer confidence and avoiding costly penalties.”
As trade policies fluctuate and environmental standards heighten, manufacturers face an increasing burden to comply with intricate regulations. And according to a recent survey by KPMG, 73% of Chief Compliance Officers (CCOs) expect regulatory expectations to rise going forward. Fortunately, automation emerges as a pivotal solution, streamlining compliance processes and empowering manufacturers to focus on growth without the looming threat of costly penalties.
This blog will explore the complexities of manufacturing compliance and demonstrate how automation can be harnessed to simplify regulatory challenges. From minimizing human error through automated workflows to ensuring seamless global operations by adapting to region-specific regulations, automation stands as an indispensable ally for manufacturers navigating the intricate world of compliance.
Regulatory Complexities Within Manufacturing
In today’s global economy, manufacturers encounter a complex web of regulatory challenges driven by shifting industrial standards and legal requirements. These challenges arise from the need to comply with diverse regulations across regions and industries. In the US, the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM) and other manufacturing associations, recently told President-elect Trump and his Cabinet about the need to address “burdensome regulations that are stifling investment, making us less competitive in the world”.
Time will tell how regulations evolve for manufacturers in the US, but what is clear is that globally, manufacturers do face a number of challenges around compliance. To sustain compliance while fostering innovation and efficiency, mastering these regulatory hurdles is essential. Two critical issues in the manufacturing industry are environmental standards and evolving trade policies, each adding layers of complexity that demand skilled management.
Environmental Standards Evolution
The evolution of environmental standards poses significant challenges for the manufacturing industry. As sustainability becomes a global priority, regulations aimed at reducing environmental impact are continually being introduced and updated. Manufacturers must adapt to stringent requirements, such as reducing emissions, managing waste, and conserving resources. These standards vary widely across regions, creating a complex compliance landscape for global operations.
Here are five top environmental standards most relevant to the industry:
- ISO 14001: This internationally recognized standard offers a framework for an effective environmental management system (EMS). It assists organizations in improving resource efficiency, reducing waste, and cutting costs while complying with stringent legal requirements.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): A European Union regulation designed to protect human health and the environment from chemical risks and improve the competitiveness of the EU chemicals industry.
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive): This directive limits the use of certain hazardous materials in electrical and electronic products, essential for manufacturers exporting to the EU.
- Clean Air Act: In the U.S., this act regulates air emissions from stationary and mobile sources to mitigate air pollution, requiring compliance from manufacturers.
- Clean Water Act: This act controls pollutant discharges into U.S. waters and sets quality standards for surface waters, vital for manufacturers potentially affecting water quality.
Non-compliance with such standards can result in hefty penalties and harm to a company’s reputation. Thankfully, according to a report by Deloitte, the manufacturing sector is making a sustained effort in adhering to environmental regulations and reducing emissions.
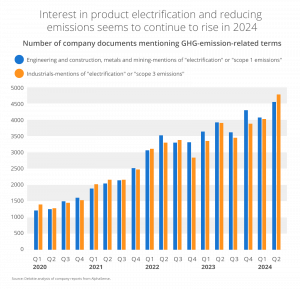
To address these issues, manufacturers are implementing more sustainable practices. Automation is key, as it allows for efficient real-time tracking and reporting of environmental data, ensuring regulatory adherence. By adopting automation, manufacturers satisfy regulatory demands and enhance environmental sustainability, positioning themselves as leaders in responsible manufacturing.
Trade Policy Shifts
Trade policy shifts present a dynamic and often unpredictable challenge for manufacturers, influencing everything from production costs to market accessibility. As governments negotiate new trade agreements and revise existing ones, businesses must navigate a constantly shifting regulatory environment. In fact, according to the Fortune/Deloitte Fall 2024 CEO Survey, international trade and tariffs are viewed as a top risk following the US presidential election.

Here are some of the key ways these shifts can impact manufacturers:
- Tariff Adjustments: Changes in trade policies often modify tariff rates, affecting the cost of imported materials and exported goods in foreign markets. This directly influences a manufacturer’s bottom line and pricing strategy.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: New or altered trade agreements can change supply chain dynamics, requiring manufacturers to source materials from different countries, leading to logistical issues and higher costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Shifting trade policies demand continuous adaptation to new compliance standards, including product labeling, safety, and environmental regulations, necessitating agile compliance strategies.
- Market Access and Competitiveness: Trade policy shifts can open new markets or restrict existing access, impacting global competitiveness and necessitating strategic market adjustments.
- Investment and Production Decisions: Policy changes affect where manufacturers invest and establish facilities. Favorable policies may encourage regional investments, while protective measures might prompt relocations.
- Innovation and Product Development: Manufacturers may need to innovate and modify products to meet the standards of new markets affected by trade policies, driving technological advancements and diversification.
To effectively navigate trade policy shifts, manufacturers must stay flexible, informed, and ready to use automation and strategic planning to mitigate risks and seize opportunities. Automation streamlines compliance processes related to trade regulations, manages documentation, tracks policy changes, and ensures products meet international standards.
How Automation Enables Compliance in Manufacturing
Automation in Compliance Tracking
Monitoring compliance is crucial for manufacturers because it helps ensure adherence to regulations, minimizing the risk of legal penalties and enhancing operational integrity. Automated accounts payable (AP) systems have emerged as vital tools for manufacturers aiming to streamline compliance tracking and ensure adherence to ever-evolving regulations.
As International Business Machines (IBM) state, “most regulators in the US and UK also now require some form of compliance monitoring.” However, traditional compliance tracking methods, often manual and error-prone, can lead to significant inefficiencies and increased risk of non-compliance. Automation addresses these issues by providing real-time, accurate compliance data and documentation.
Here are some of the top ways accounts payable automation assists in compliance:
- Automatic Verification of Tax Codes: Automated AP systems validate tax codes in real-time, ensuring transactions comply with tax regulations locally and internationally, reducing costly tax errors and improving financial reporting accuracy.
- Efficient Generation of Audit-Ready Reports: These systems automatically produce comprehensive reports, simplifying audit preparation. With accurate records, manufacturers can swiftly respond to auditor requests, reducing audit-related stress and resource use.
- Seamless Integration with Compliance Protocols: Automated AP systems integrate with compliance protocols, creating a unified platform to manage regulatory requirements, ensuring consistent regulation adherence without manual input.
- Real-Time Compliance Monitoring: AP automation offers real-time monitoring and alerts for compliance issues, enabling prompt resolution of potential non-compliance, mitigating risks before they escalate significantly.
- Enhanced Data Security and Access Control: These systems incorporate advanced security features to protect sensitive financial data, ensuring only authorized access, preventing data breaches, and maintaining compliance with data protection regulations.
By leveraging AP automation, manufacturers can ensure they meet all necessary regulations while simultaneously focusing on strategic growth initiatives. This technological advancement not only supports operational efficiency but also enhances the ability to swiftly adapt to regulatory changes, ensuring sustained compliance in an ever-evolving landscape.
Reducing Human Error with Accounts Payable Automation
In the manufacturing sector, minimizing errors is crucial for maintaining compliance and quality standards. Human error, often stemming from manual processes and repetitive tasks, can lead to costly compliance breaches and operational inefficiencies. According to Forbes, the financial cost of downtime on Global 2000 companies is estimated to be $400 billion annually.
The direct costs include lost revenue, regulatory fines, and penalties for missed service level agreements (SLAs). Accounts Payable Automation for manufacturing significantly reduces these risks by standardizing processes and eliminating the variability associated with human intervention.
Here are key ways in which AP Automation helps reduce the risk of human error:
- Streamlined Document Management: Automated workflows efficiently handle tasks like invoice processing and approval routing, reducing errors common in manual handling.
- Standardized Processes: Automation standardizes AP processes across the organization, minimizing oversight and discrepancies by reducing reliance on individual judgment.
- Improved Accuracy in Data Entry: Automated AP systems ensure bills, invoices, and payments are recorded accurately, lessening errors from manual entry, such as typos or missed entries.
- Automated Verification and Matching: These systems automatically match invoices with purchase orders and delivery receipts, highlighting inconsistencies and preventing payment errors.
- Real-Time Error Detection and Reporting: AP automation identifies and reports errors in real-time for immediate correction, aiding compliance and avoiding disruptions.
- Enhanced Audit Trails: Automated systems document every transaction and change, creating comprehensive audit trails that simplify compliance and audit processes.
By implementing AP automation, manufacturers can significantly lower the risk of human error, ensuring smoother operations and robust compliance with regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Automated Accounts Payable Systems for Global Compliance
Manufacturers aiming for efficient, compliant operations on a global scale can greatly benefit from accounts payable automation. As companies expand internationally, they encounter various regulatory environments with distinct compliance requirements. According to Forbes, there are 20 essential steps that businesses should take when scaling into international markets.
However, manually navigating these complexities is challenging and prone to errors. Automated AP systems seamlessly manage financial transactions while ensuring adherence to international regulations and standards.
Here’s how AP automation supports manufacturers in maintaining global compliance:
- Uniform Application of Global Standards: Automated AP systems ensure consistent compliance across all operations, maintaining adherence to global financial regulations and preventing discrepancies from manual processes.
- Automated Currency Conversion and Tax Compliance: These systems automatically adjust transactions for currency and tax compliance, essential for handling multiple currencies and tax jurisdictions, reducing errors and penalties.
- Efficient Cross-Border Transactions: Automation streamlines cross-border transactions by managing time zones, languages, and regulations, minimizing delays and ensuring compliance with international laws.
- Centralized Regulatory Updates: Systems are centrally updated to reflect international law changes, ensuring that all branches operate under up-to-date regulations and reducing the manual updating burden.
- Enhanced Due Diligence and Fraud Detection: Automated AP systems conduct thorough transaction checks, using analytics and AI to detect fraud, ensuring secure and compliant operations.
- Scalable Solution for Multi-National Operations: As manufacturers grow globally, automated systems provide scalable solutions that adapt to increasing transaction complexity while maintaining strong compliance controls.
By integrating automated accounts payable systems, manufacturers can effectively manage the complexities of global compliance, ensuring that all operations are synchronized with international standards while focusing on innovation and market expansion.
Proactive Compliance with Accounts Payable Automation
Proactive compliance through automation transforms how manufacturers anticipate and manage regulatory changes. Unlike reactive strategies that tackle compliance issues post-factum, proactive compliance uses automation to predict and adjust to new regulations in real-time. Automating accounts payable processes is key for manufacturers to maintain proactive compliance. Here are ways to achieve it:
- Predictive Analytics for Regulatory Changes: Automated AP systems utilize predictive analytics to forecast regulatory shifts by examining historical data and trends, providing advance notice to adapt practices for compliance.
- Automated Compliance Updates and Alerts: These systems automatically update protocols and generate alerts for new regulations, ensuring timely compliance adjustments and alignment with current legal requirements. According to Forbes, this feature is somewhat of a “force multiplier” as it serves as a persistent watchdog for regulation changes that impact your organization and also identifies applicable requirements, even updating policies and controls to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Streamlined Documentation and Record-Keeping: Automation keeps records organized and accessible, crucial for compliance audits and regulatory checks, enhancing transparency and minimizing non-compliance risks.
- Risk Management and Mitigation: Automated systems pinpoint compliance risks in AP processes, allowing manufacturers to proactively counter issues, thus reducing chances of fines or reputational damage.
- Cross-Functional Integration: By linking AP automation with other systems, compliance data is shared seamlessly across departments, fostering organization-wide regulatory adherence.
- Continuous Process Improvement: As systems gather compliance performance data, it informs process refinements, ensuring compliance practices keep pace with regulatory changes and operational efficiency.
By adopting accounts payable automation, manufacturers not only streamline their financial operations but also build a robust, proactive compliance framework. This approach supports sustained regulatory adherence, minimizes risks, and allows manufacturers to focus on strategic objectives without the constant worry of regulatory breaches.


