The manufacturing industry is experiencing a technological transformation, with innovative manufacturers rapidly adopting advanced technologies to secure their operations and boost competitiveness in a constantly changing market. According to the Deloitte 2025 Manufacturing Industry Outlook, 98% of surveyed manufacturers have started their digital transformation journey. As businesses seek competitive advantages and new efficiencies, automation has emerged as the driver of technological innovation and operational excellence. The integration of advanced automation technologies such as robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI) has ushered in an era of “smart manufacturing”.
In this blog, we will explore how these innovations are streamlining production processes, enhancing product quality, and offering scalable solutions to overcome the high costs of implementation. We will also examine how automation facilitates data-driven decisions for continuous improvement and discuss the future of manufacturing innovation, including groundbreaking concepts like predictive maintenance and digital twins, which promise next-level efficiency.
The Era of Smart Manufacturing
What is Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing enhances efficiency, flexibility, and sustainability by utilizing the latest technologies. It leverages advanced equipment and software like robotics, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) to accelerate production and quickly adapt to changes. According to Forbes, “smart manufacturing brings together cutting-edge technologies and puts them to work on the shop floor“. This approach streamlines operations and minimizes waste, supporting real-time, data-driven decisions, and offering businesses a significant competitive edge.
Smart Manufacturing Technologies:
Robotics and AI
Integrating robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) within the manufacturing industry is transforming production processes by combining the strengths of both technologies. Robotics enhances precision and consistency by performing repetitive and physically demanding tasks, while AI brings intelligence to these systems, enabling them to adapt and optimize in real-time.
According to McKinsey, AI adoption worldwide has increased dramatically in the last year to 72% as organizations begin to discover its many advantages.
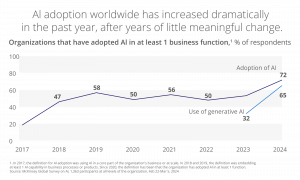
Together, robotics and AI drive efficiency and innovation, offering several key benefits for manufacturers:
- Increased Productivity: Automating tasks allows for continuous operation, significantly boosting output and freeing human workers for more skilled roles.
- Enhanced Quality Control: AI algorithms detect defects early by analyzing data, ensuring high product standards are consistently met.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By minimizing waste and optimizing resource use, manufacturers can lower production costs.
- Improved Flexibility: Automated systems can quickly adapt to changes in production demands, allowing manufacturers to respond swiftly to market needs.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered predictive analytics anticipate equipment failures, reducing downtime, maintenance costs and prolonging equipment life.
As manufacturers embrace this technology, they gain a competitive edge, ensuring scalability and adaptability in a fast-evolving market. The future of manufacturing relies on this synergy, driving innovation and efficiency across the industry.
Role of IoT in Manufacturing
The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a pivotal role in smart manufacturing by connecting devices, machines, and systems to streamline operations. This connectivity allows for real-time data collection and analysis across manufacturing operations, paving the way for more informed decision-making and strategic planning. IoT’s integration in manufacturing brings several benefits:
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: IoT provides real-time monitoring and control, reducing downtime and optimizing production efficiency.
- Improved Predictive Maintenance: IoT analyzes sensor data to predict equipment failures, allowing maintenance before breakdowns, minimizing stoppages, and extending equipment lifespan.
- Quality Control and Assurance: IoT devices analyze production data, detecting and correcting deviations from quality standards promptly.
- Supply Chain Optimization: IoT improves visibility into inventory and schedules, enhancing supply chain coordination and reducing excess stock.
- Energy Efficiency: IoT monitors energy patterns, optimizing use and helping achieve sustainability goals.
With these capabilities, IoT enhances operational efficiency and supports manufacturers in meeting sustainability goals. As the industry becomes more data-driven, IoT’s role is growing, ensuring a more agile production environment that aligns with evolving market demands.
How Does Automation Streamline Manufacturing Processes?
Eliminating Inefficiencies
Automation in manufacturing plays a crucial role in significantly reducing inefficiencies by optimizing workflows and minimizing human error. Here are the ways automation achieves this:
- Consistent Precision in Repetitive Tasks: Automated systems perform repetitive tasks with high precision, enhancing productivity and freeing human resources for complex problem-solving roles. According to Forbes, smart machines are becoming more prevalent in factories, increasing production and reducing errors. They are bound to enable further automation beyond the assembly line in time.
- Continuous Operation of Production Lines: Automation facilitates uninterrupted production, reducing idle time and improving throughput.
- Dynamic Production Scheduling: Real-time data utilization allows for dynamic adjustments to production schedules, closely aligning operations with demand fluctuations, and reducing overproduction and inventory costs.
- Early Defect Detection: Automated quality control systems detect defects early in the production process, minimizing waste and ensuring high product standards.
As a result, automation not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to cost savings, increased production speed, and improved overall competitiveness in the manufacturing sector.
Enhancing Product Quality
Automation is essential in enhancing product quality within manufacturing processes. By utilizing technologies such as robotics and AI, automation ensures precision and consistency in production. Here are the ways automation enhances product quality:
- Reduced Human Error: Automation minimizes human error by ensuring precise and consistent production standards.
- Stringent Quality Control: Automated systems monitor production in real time, quickly addressing deviations from standards.
- Predictive Analytics: Automation uses predictive analytics to anticipate and prevent defects.
- Data Collection Through IoT: IoT devices collect data on product performance and quality throughout the lifecycle.
- Continuous Improvement: This data-driven approach enables ongoing refinement of processes and product designs using empirical evidence.
As a result, automation not only meets but often exceeds quality expectations, enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering brand loyalty. Consequently, manufacturers can maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly quality-conscious market.
Navigating the Barriers to Automation in Manufacturing
Automation in manufacturing presents immense opportunities for efficiency and innovation, yet significant barriers, like cost and scalability, remain. Many businesses find the initial expense of implementing automation technologies intimidating, necessitating strategic foresight and financial planning. By pursuing scalable solutions, manufacturers can navigate these hurdles, aligning their automation efforts with current capabilities and future growth aims.
Overcoming High Implementation Costs
Overcoming high implementation costs of automation in manufacturing is crucial for many businesses seeking to improve efficiency and productivity. Here are several ways manufacturers can manage and reduce these financial hurdles:
- Adopt a Phased Approach: Gradually integrate automation to spread costs, focusing initial investments on high-impact areas for quick efficiency gains and savings.
- Leverage Government Incentives and Subsidies: Utilize support designed to foster technological advancement in manufacturing.
- Collaborate with Technology Providers: Flexible financing options, like leasing or pay-as-you-go models, can ease financial strain.
- Conduct Cost-Benefit Analysis: Choose effective automation tools to ensure strategic alignment with business goals, maximizing benefits.
As manufacturers achieve efficiency improvements and operational savings, these results can offset initial expenses, making the transition to automation a feasible and economically sustainable strategy.
Scalable Automation Solutions
In the dynamic manufacturing landscape, scalable automation solutions are essential for maintaining flexibility and supporting growth. They enable manufacturers to align technology investments with current needs and future expansion. Yet, scaling automation can be difficult to achieve. Forbes reports that the percentage of automated processes between 2023 and 2024 remained flat, despite continued IT investment. Visibility and control into existing processes is a crucial starting point. Once this is achieved, there are a number of ways to implement scalable solutions and their benefits:
- Utilize Modular Robotics and Cloud-Based Platforms: These scalable technologies evolve with the business, providing a flexible foundation for automation.
- Mitigate Risks: Phased automation reduces risks of large-scale deployments, enabling process adaptation based on performance outcomes.
- Automate Select Processes First: Targeting high-efficiency areas initially secures substantial gains and allows progressive system integration.
- Ensure Compatibility with Existing Systems: This minimizes the need for extensive overhauls, reducing associated costs and disruptions.
With scalable automation, manufacturers strike a balance between securing immediate advantages and meeting long-term strategic objectives, achieving sustainable growth and ongoing improvements in automation.
Intelligent Automation in Manufacturing
Leveraging Automation for Continuous Improvement
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, leveraging automation for actionable insights is crucial for continuous improvement and staying competitive. Automated systems provide real-time analytics to identify inefficiencies and quickly implement corrective actions. Utilizing AI and machine learning, automation analyzes large datasets to reveal patterns and predict trends. This data-driven approach empowers manufacturers in various ways:
- Real-Time Insights and Analytics: Automation systems provide continuous data streams to identify inefficiencies, enabling timely interventions.
- Pattern Recognition and Trend Prediction: AI and machine learning allow manufacturers to analyze large data volumes, detecting patterns and forecasting developments.
- Proactive Decision-Making: Automation supports informed decisions by continually refining production processes through data analysis.
- Support of Lean Manufacturing Principles: Automation minimizes waste, streamlines operations, and optimizes resource use.
- Adaptation to Market Demands: Real-time feedback enables swift adjustments to market changes, maintaining quality and efficiency.
Moreover, automation cultivates a culture of continuous improvement by equipping employees with the tools and insights necessary to enhance their workflows. According to McKinsey, by next year smart workflows will become standard across most organizations and employees will use data to optimize nearly every aspect of their work. As a result, businesses can uphold operational excellence and foster innovation, setting the stage for sustained growth and success in a constantly evolving industrial landscape.
Future Trends in Manufacturing
What Lies Ahead in Manufacturing?
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, new technologies promise to redefine productivity, efficiency, and innovation. Among these emerging trends, predictive maintenance and digital twins stand out as key enablers of the next generation of manufacturing processes. These technologies are not only enhancing current operations but are also setting the stage for future developments that will shape the industry for years to come.
Predictive Maintenance: Transforming Equipment Management
Predictive maintenance is set to revolutionize manufacturing by allowing companies to anticipate and prevent equipment failures, thus enhancing operational fluidity and reducing costs associated with unexpected breakdowns. Here’s how predictive maintenance is making an impact:
- Proactive Intervention: Utilizes data analytics to foresee equipment malfunctions before they occur, enabling timely interventions and maintaining continuous production flow.
- Extended Machinery Lifespan: Regular assessments and maintenance prevent excessive wear and tear, extending the life of machinery.
- Downtime Reduction: Anticipating failures reduces unplanned stoppages, ensuring a smoother manufacturing process.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces expenses related to emergency repairs and associated production delays.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous data collection and analysis facilitate ongoing surveillance of equipment health.
As predictive maintenance strategies become more sophisticated, their integration into daily operations will further enhance efficiency and reliability within manufacturing environments.
Digital Twins: Pioneering Virtual Replication
Digital twins are reshaping the manufacturing industry by offering virtual counterparts to physical assets, allowing for enhanced simulation, analysis, and optimization. With Deloitte reporting that up to 1.9 million manufacturing jobs could remain unfilled by 2033, the importance and presence of digital twins in manufacturing is likely to increase.
This increased importance and presence is already being reported by McKinsey, with 86% of respondents saying digital twins are applicable to their operations and 44% saying they have already implemented digital twins.
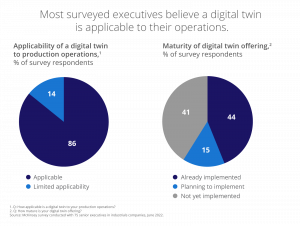
Here’s how digital twins are driving transformation:
- Process Simulation: Virtual replicas enable the testing and perfecting of processes without disrupting physical operations.
- Outcome Prediction: Digital twins allow manufacturers to foresee potential outcomes and make data-driven operational adjustments with precision.
- Operational Optimization: Offers a platform to refine procedures, boosting productivity and operational quality.
- Performance Insights: Real-time data offers insights into system performance, facilitating strategic decision-making.
- Risk Mitigation: Virtual modeling capabilities help identify and address potential issues before they impact production.
By continuously evolving, digital twins promise to further integrate into manufacturing systems, leading to smarter, more adaptive, and innovative production environments that keep pace with the challenges of a dynamic market.
Conclusion
Automation and AI are at the forefront of technological innovation in manufacturing, driving significant changes in production processes and operational strategies. While the benefits are substantial, including increased efficiency and competitiveness, manufacturers must navigate challenges related to investment costs, integration complexities, and workforce adaptation. Staying informed about these trends is crucial for industry stakeholders aiming to leverage automation technologies effectively.


