Although the shift towards digital formats of invoicing can improve efficiency, electronic copies alone aren’t always enough. As companies transition to digital processes, there’s a growing trend toward e-invoicing to standardize and streamline financial transactions while accelerating processing and reporting. At the same time, more governments are mandating e-invoicing to ensure accurate tax reporting and reduce fraud.
Let’s take a closer look at e-invoicing, its benefits, the trends driving adoption, and what you need to do to get started.
What Is E-invoicing?
E-invoicing is the exchange of invoices between suppliers and buyers in a structured electronic format rather than by paper. Standardization of e-invoice formats streamlines invoice processing and creates an accessible input to automate invoice processing, reconciliation, approval, and data integration with accounting systems. This can support increasing volumes of invoices, for example for B2B companies.
Through e-invoicing, data is machine-readable and can be imported into a buyer’s AP system without requiring manual intervention. The European standard on e-invoicing (EN16931), for instance, defines a core invoice model that must be used, although additional information may be added in some cases.
Structural components include:
- Formats such as XML or EDI that contain consistent fields for processing
- Digital signatures and authentication to ensure data integrity
- Compliance with relevant taxing authorities in each country or region
- Integration with supplier and buyers AP and ERP systems
- Support for real-time validation of invoice data
E-invoicing does not include digital invoices like PDFs or email attachments, which have unstructured data that needs to be extracted, for example using optical character recognition (OCR). Adopting e-invoicing eliminates the need for OCR because the data arrives digitized and can directly populate a procure-to-pay system.
Regional differences in e-invoicing add to the complexity of compliance – for example in Latin America where countries require real-time invoice clearance vs. the EU, where invoices are audited after payments are made. Gartner expects a global shift towards real-time clearance, where invoices are checked and approved by a central government agency before payment.
Instead of spending time researching invoice regulations and tax mandates, you can send and receive uniform and compliant e-invoices by joining e-invoicing networks. Global e-invoicing networks bring businesses together with their vendors and financial institutions to support compliant and automated e-invoice exchange. The technological framework supports transaction visibility and international trade.
Trends Driving e-invoicing Adoption
The cross-border B2B market is forecast to grow 120% from 2023 to 2030. Cross-border transactions increase the complexity of invoicing and each country has a unique approach to requirements and tax policies. For example, while the E.U. has a standard data model and formatting for its member countries, the value-added tax (VAT) rates are different in each nation. e-invoicing helps to ensure accuracy in tax calculations.
Major trends include:
Government Regulations and Mandates
Increasingly, countries are mandating e-invoicing to facilitate tax compliance and real-time reporting to government tax authorities. Governments see these regulations as a way to reduce fraud in the system, increase compliance, and raise revenue.
Increasing Focus on Digital Transformation and Automation
EY’s survey of 1,200 global CEOs showed that digital transformation remains imperative to drive long-term success. 58% of CEOs said they are planning to accelerate the transformation of their business operations in 2024.
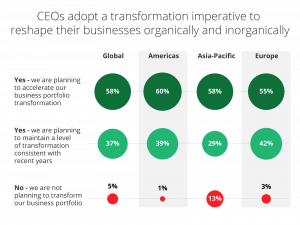
SOURCE: EY CEO Outlook Pulse Survey — January 2024
Real-Time Cash Flow Visibility
Cash flow remains the number one reason businesses fail. E-invoicing can support faster processing so that invoices can be approved in hours rather than days or weeks using traditional methods. This provides greater transparency into cash flow for more accurate forecasting.
Pressure to Reduce Cost and Improve Efficiency
Companies are continuing to feel the effects of inflationary pricing, higher interest rates, and fluctuating customer demand. A Q1 2024 survey by the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis showed that more businesses saw revenue declines than increases last year and the majority expect continued declines in 2024.
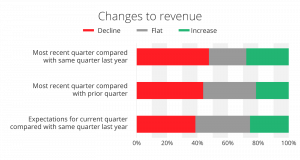
SOURCE: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, General Business Conditions Survey 2024
Cost-cutting is top of mind for many companies these days and efficiency is driving change. Shifts to remote purchasing, particularly in B2B, are also accelerating the need for more sophisticated touchless processes to achieve efficiency and lower costs.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Businesses are also looking to meet aggressive sustainability goals. Of the world’s 2,000 largest, publicly-listed companies, half have set net-zero targets. Reducing waste and paperwork helps meet sustainability goals.
E-invoicing Timelines Globally
More than 100 countries already have some form of e-invoice or continuous transaction control (CTC) requirements for B2B or B2G transactions. E-invoices are often integrated within CTCs enabling tax authorities to gather transaction data directly from a company’s accounting systems for VAT compliance checks.
Most countries have adopted a multi-phase approach to mandates with thresholds for different sized businesses or invoices amounts. Italy was the first country in the EU to implement widespread mandates for mandatory e-invoicing, with the latest directive in January 2024 applying to smaller businesses. New requirements are regularly updated and several countries have pending legislation. Here is a sampling of the latest implementation timelines by country.
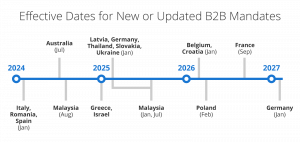
Note: Table is a sampling of timelines for certain countries and may be subject to change or delays
By 2030, it’s expected that the majority of the 200 counties that have value-added taxes will have mandatory controls in place necessitating e-Invoices.
E-invoicing in the U.S.
Although electronic invoicing is not mandated federally in the U.S., these changes impact American companies that do business internationally or want to optimize their invoicing expenses.
There are also some use cases where e-invoicing is required. For example, Section 1008 of the National Defense Authorization Act of FY 2001 mandates electronic invoice submission for contractors working with the U.S. Department of Defense. State contractors in California must also submit e-invoices through the Cal eProcure system.
Nationally, the Digital Business Networks Alliance (DBAlliance) is a nonprofit working to establish a standardized exchange framework for straight-through processing between service providers and suppliers. In March, it announced the first successful transfer of an invoice through the Open Exchange network. The DBAlliance is supported by Microsoft, SAP, Chevron, ConocoPhillips, Halliburton and 25 other member organizations.
The Benefits of E-invoicing
While e-invoicing is not yet a universal requirement, the benefits are. Adopting e-invoicing practices allows companies to compete and stay compliant in the global marketplace.
- Fewer errors and delays – When data follows standard formats and is machine-readable, it reduces the risk of human error and resulting delays. Enhancing the accuracy and validation of invoices can improve processing times, especially when dealing with manual processes.
- Environmental benefits – E-invoicing reduces the amount of paper and also saves on resources. Digital processing eliminates the need to mail invoices, reducing the amount of handling and greenhouse gas emissions from transportation and delivery.
- Improved tax compliance – Accurate data supports precise tax calculations. Government clearance before payment can ensure compliance with applicable tax regulations.
- Auditable trail – An electronic trail that tracks changes is accessible and fully auditable.
Getting Started with e-invoicing
Getting started with e-invoicing requires collaboration across multiple disciplines within your organization. Finance, procurement, legal, and technical teams will need to work together to create an efficient system, including:
- Integration with AP systems
- Ensuring compliance with evolving country requirements
- Creating internal policies and procedures
- Onboarding suppliers
- Mapping data from existing customer databases
You will also need to develop a change management plan to help your team adapt to new systems, including training and education.
Stay competitive in a world demanding e-invoicing. Partnering with an end-to-end automated procure-to-pay solution streamlines your e-invoicing journey, ensuring compliance, efficiency, and significant cost savings. Automation powered by machine learning can reduce invoice processing costs by up to 90%.


