More than 100 countries now require some form of e-invoicing, with new regulations rapidly emerging. Italy and Germany have led the charge in Europe with comprehensive mandates, while frameworks expand globally. Keeping pace with regulatory changes is key to maintaining your business’s competitiveness and compliance.
E-invoicing, or electronic invoicing, plays a critical role in today’s digital environment. It streamlines financial processes, enhances transaction speed and accuracy, and provides immediate insights. Governments are implementing these mandates to strengthen tax compliance and prevent fraud.
In this e-book, we’ll take a deep dive into e-invoicing, its benefits, uncover the trends driving adoption, explore current regulations, and provide strategic steps to ensure your business remains at the forefront.
What is E-Invoicing?
E-invoicing digitizes the invoicing process, removing reliance on paper. It facilitates the exchange between suppliers and buyers in a structured digital format, which according to EU guidelines, ensures automatic reading and processing, boosting accuracy and efficiency.
The main objective of e-invoicing is to enhance the invoicing process, cut costs, and improve cash flow. Automated systems offer businesses faster processing with fewer errors, while also supporting tax compliance and reducing fraud risks.
E-invoicing delivers machine-readable data, easily imported into a buyer’s AP system without requiring manual intervention. The European standard (EN16931), for instance, outlines a core model that must be used, although additional information may be added in some cases.
Key components include:
- Formats such as XML or EDI that contain consistent fields for processing
- Digital signatures and authentication to ensure data integrity
- Compliance with relevant taxing authorities in each country or region
- Integration with supplier and buyers AP and ERP systems
- Support for real-time validation of invoice data
E-invoicing excludes digital formats like PDFs or email attachments, which have unstructured data that needs to be extracted, for example using optical character recognition (OCR). Adopting e-invoicing eliminates the need for OCR because the data arrives digitized and can directly populate a procure-to-pay system.
Regional differences in e-invoicing add to the complexity of compliance – for example in Latin America where countries require real-time invoice clearance vs. the EU, where invoices are audited after payments are made. Gartner expects a global shift towards real-time clearance, where invoices are checked and approved by a central government agency before payment.
Instead of spending time researching invoice regulations and tax mandates, you can send and receive uniform and compliant e-invoices by joining e-invoicing networks. Global e-invoicing networks bring businesses together with their vendors and financial institutions to support compliant and automated e-invoice exchange. The technological framework supports transaction visibility and international trade.
Navigating PEPPOL and Other Global E-Invoicing Frameworks
Regional differences in e-invoicing add to the complexity of compliance, as observed in various government mandates worldwide. While PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement Online) is a leading e-invoicing network, particularly for cross-border transactions within and beyond the EU, it is just one of several prominent frameworks in use across Europe and worldwide.
Understanding PEPPOL: A Game-Changer in Global E-Invoicing
PEPPOL was developed to streamline public procurement processes across Europe and has since grown into a widely adopted network for exchanging structured e-documents. It uses a standardized four-corner model where senders and receivers connect through Access Points, ensuring secure, compliant, and automated invoice exchange. PEPPOL supports documents such as invoices, credit notes, and shipping notices using the PEPPOL BIS XML format.
Key benefits of PEPPOL include:
- Eases cross-border transactions: PEPPOL standardizes national e-invoicing through an interoperable framework.
- Boosts security and compliance: Its network securely transmits data, meeting EU regulatory needs.
- Supports diverse business documents: PEPPOL handles invoices, purchase orders, credit notes, and more.
- Extensive adoption and growth: While not mandatory globally, PEPPOL is increasingly vital for international businesses.
- Visibility in the supplier network: Directories help companies verify PEPPOL support, easing onboarding and exchanges.
However, PEPPOL is not the only standard—different countries and regions have implemented their own frameworks tailored to national regulations and requirements.
Other Major E-Invoicing Frameworks
As EU countries advance e-invoicing mandates, a range of national formats has emerged alongside the pan-European PEPPOL framework. While PEPPOL BIS Billing 3.0 offers a standardized model for cross-border invoicing, many regions continue to enforce local formats to meet specific regulatory and operational needs. Understanding how these formats align or differ from PEPPOL is essential for ensuring compliance and driving efficiency across markets.
- Germany: XRechnung and ZUGFeRD
As Germany advances towards comprehensive e-invoicing implementation, businesses need to be informed about the key formats driving compliance and efficiency in the region:
- XRechnung: As the mandated format for B2G transactions, XRechnung follows the European standard (EN16931), offering a machine-readable XML-based structure, and making it a cornerstone for broader B2B adoption starting in 2025.
XRechnung is closely aligned with PEPPOL BIS Billing 3.0 and can be transmitted via the PEPPOL network.
- ZUGFeRD: Serving as an effective bridge to digital compliance, ZUGFeRD integrates PDF for readability with XML for automated processing, becoming increasingly popular for B2B transactions.
ZUGFeRD is not natively supported by PEPPOL due to its hybrid format combining human- and machine-readable elements.
- Italy: Sistema di Interscambio (SdI) and FatturaPA
Italy was an early adopter of mandatory e-invoicing, requiring all B2B and B2G invoices to be submitted via the government’s Sistema di Interscambio (SdI) platform in the FatturaPA XML format. This model enables real-time validation by tax authorities and has become a benchmark for structured invoice clearance models.
FatturaPA is not PEPPOL-compliant and operates under a clearance model, in contrast to PEPPOL’s post-audit approach.
- Spain: Facturae
Spain’s Facturae format, used in conjunction with the Punto General de Entrada de Facturas Electrónicas (FACe) platform, is mandated for B2G transactions and forms the basis for its evolving B2B e-invoicing strategy. A broader mandate is expected by 2027. Facturae supports digital signatures and ensures direct integration with public administrations.
Facturae is a domestic format and requires conversion for use within the PEPPOL network.
- Finland and Sweden: Teapps and Finvoice
In the Nordic region, Finland and Sweden have long embraced voluntary B2B e-invoicing.
- Teapps: This XML-based format is supported by local banks and widely used for efficient invoice processing in domestic markets.
Teapps is not part of the PEPPOL standard but is used alongside it for local transactions.
- Finvoice: Like Teapps, Finvoice is an XML-based format that facilitates efficient invoice management, operating alongside PEPPOL BIS for increased compatibility.
Finvoice is supported for domestic use and increasingly supplemented by PEPPOL for cross-border interoperability.
Choosing the Right Framework for Your Business
While PEPPOL offers a robust and growing international network, companies operating in specific countries may also need to support local standards like FatturaPA, XRechnung, or Finvoice to remain compliant. The optimal approach often includes:
- Multi-framework capability: Supporting various formats based on customer or regulatory requirements
- Access Point integration: Leveraging PEPPOL for standardized, cross-border exchange
- Localization flexibility: Adapting to country-specific mandates and validation systems
The Role of Certified E-Invoicing Service Providers
Certified service providers like SoftCo play a crucial role in streamlining e-invoicing adoption across diverse regulatory environments. As businesses increasingly operate across borders—and within jurisdictions that mandate different e-invoicing standards—these providers help ensure secure, compliant, and efficient document exchange.
While PEPPOL is a key cross-border network in Europe, providers must also support standards like XRechnung, ZUGFeRD, FatturaPA, Facturae, Finvoice, and Teapps. Successfully navigating these requires both technical prowess and regulatory insight.
Partnering with an experienced provider like SoftCo brings key benefits:
- Secure and Compliant Connectivity: Gain reliable access to e-invoicing networks, ensuring top-tier data security and privacy.
- Simplified Onboarding and Integration: Seamless technical setup, including PEPPOL ID registration and ERP/AP system integration.
- Regulatory Agility: Stay ahead of evolving mandates, adapt swiftly to compliance changes.
- Support for Multiple Frameworks: Issue and receive invoices across standards like PEPPOL BIS, FatturaPA, and Finvoice.
- Cross-Border Expertise: Minimize delays and non-compliance with expert knowledge of international invoicing workflows.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation and validation boost invoice accuracy and streamline processing.
In a fragmented global e-invoicing environment, certified service providers offer a unified, expert-driven solution—accelerating digital transformation while ensuring compliance and scalability across markets.
Trends Driving E-Invoicing Adoption
The global cross-border B2B payments market was valued at approximately USD 196 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 7.4 % through 2030, reaching over USD 300 billion. As global supply chains expand and digital trade accelerates, the volume and complexity of cross-border invoicing continues to rise. Each country applies its own tax rules, clearance models, and compliance mandates—creating operational challenges for finance teams. For example, while the EU enforces a common data standard (EN16931), VAT rates and clearance processes still vary across member states.
E-invoicing is now crucial for keeping financial operations smooth, compliant, and ready for the future. It enables quick tax checks and pushes digital change forward, making its advantages clear. In 2025, five key trends are driving widespread adoption of e-invoicing, making it a key part of modern business plans.
- The Shift Towards Digital Transformation
- Government Regulations and Mandates
- Integration with Cloud Technologies
- Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
- Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
The Shift Towards Digital Transformation
Digital transformation continues to be a powerful force reshaping how businesses operate—and is emerging as a foundational component of that shift.
According to McKinsey, 90% of organizations are undergoing some form of digital transformation, highlighting its widespread impact across industries.
As companies modernize finance functions, streamline workflows, and reduce manual effort, e-invoicing is increasingly viewed as a strategic enabler of:
- Real-time data access
- Automation
- Compliance
Deloitte’s research reinforces this momentum, noting, 98% of companies have already begun their digital transformation journey, underscoring how universal and urgent this shift has become.
Additionally, PwC reports:
- 49% of tech leaders have fully integrated AI into their business strategy
- AI integration is often applied in invoicing, payments, and reporting functions
- These investments help reduce processing times, eliminate human error, and provide more accurate, actionable insights.
Digital transformation is no longer optional—it is central to maintaining competitiveness in a fast-moving global economy. By embedding e-invoicing into broader digital strategies, businesses can:
- Accelerate financial operations
- Support cross-border trade
- Ensure compliance with emerging regulatory mandates
Integration with Cloud Technologies
Cloud adoption is accelerating e-invoicing implementation by enabling scalable, secure, and seamless financial processes. According to PWC’s Cloud and AI Business Survey, organizations are experiencing a number of benefits from investments in cloud technologies, including:
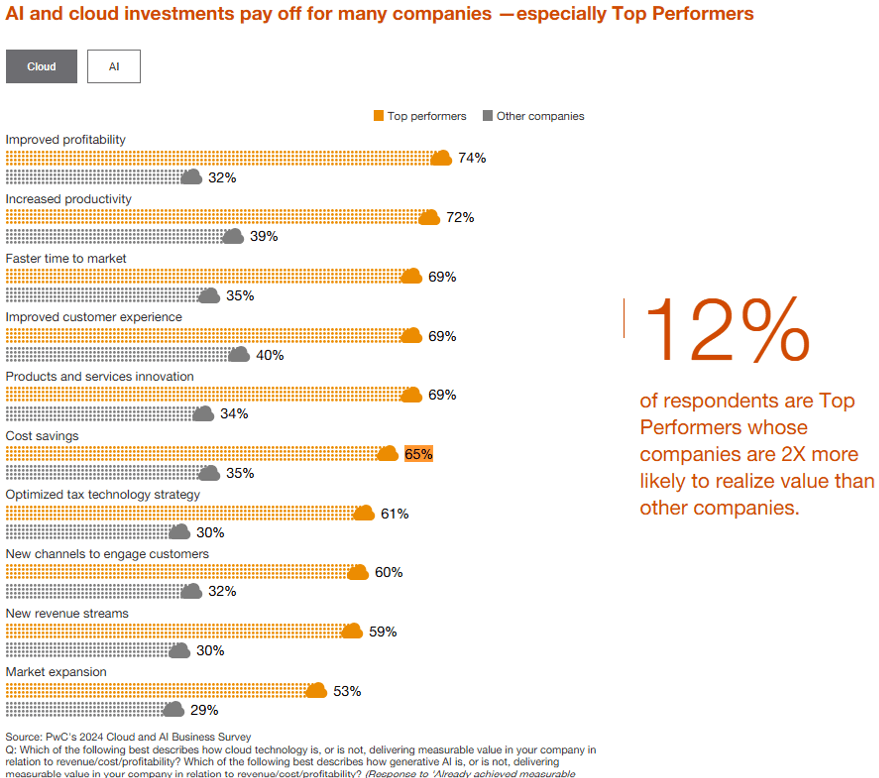
Cloud platforms provide the flexibility to handle growing invoice volumes and integrate smoothly with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, ensuring real-time access to accurate financial data.
These capabilities support:
- Faster invoice processing
- Reduced manual errors
- Enhanced compliance with evolving tax regulations across multiple jurisdictions
Additionally, cloud-enabled automation streamlines workflows by reducing manual intervention in accounts payable and receivable functions, accelerating payment cycles and improving cash flow management. The security and reliability of cloud infrastructure also ensure sensitive financial information is protected while facilitating seamless collaboration between suppliers, buyers, and tax authorities.
Together, these advantages make cloud integration a foundational trend driving widespread e-invoicing adoption, empowering businesses to modernize finance operations and maintain competitiveness in a rapidly digitizing global economy.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
Financial pressure from persistent inflation, rising interest rates, and demand volatility has made cost-cutting a top priority in 2025. E‑invoicing is gaining traction as a powerful lever to streamline operations, reduce expenses, and reallocate resources.
According to Billentis, by adopting electronic and automated invoice processes, businesses can achieve cost reductions of 60-80%, with a return on investment within 0.5 to 1.5 years.
EY also highlights that using e‑invoicing with real-time reporting can significantly reduce VAT compliance workload, decrease human error, improve cash flow visibility.
As a result, organizations are:
- Reducing labor costs: Automation cuts time spent on data entry, validations, and exceptions.
- Accelerating cash flow: Faster invoice approvals and VAT clearance enhance liquidity.
- Minimizing errors and risk: Fewer duplicates, fraudulent charges, and tax penalties.
- Boosting strategic capacity: Finance teams can shift focus to analysis, planning, and exception handling.
E‑invoicing is rapidly evolving from a compliance tool into a strategic finance asset—empowering businesses with leaner operations, smarter resource allocation, and significant impacts on the bottom line.
Sustainability as a Driver for Adoption
Sustainability is a growing catalyst for e-invoicing adoption, as organizations seek to meet both environmental goals and regulatory demands.
The Billentis Global E-invoicing and Tax Compliance Report highlights the significant environmental benefits of transitioning from paper-based invoicing to digital processes, including:
- Substantial reduction in paper consumption: Each paper invoice typically uses 2.5 sheets, and about 3,000 invoices equate to one tree saved.
- Lower carbon footprint: E-invoicing reduces CO2 emissions by at least 40 grams per invoice by eliminating paper production, printing, transportation, and disposal.
- Waste reduction: Digital invoices cut down on paper waste and related disposal issues.
These environmental advantages contribute directly to corporate social responsibility (CSR) and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) commitments. The report also notes that regulatory frameworks such as the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) require companies to provide reliable data on environmental impact, a need effectively supported by e-invoicing systems.
Complementing this, PwC’s Global CSRD Survey reveals that companies recognize multiple business benefits from sustainability reporting, including:
- Better environmental performance (51%)
- Improved stakeholder engagement (49%)
- Risk mitigation (48%)
- Cost savings (26%)
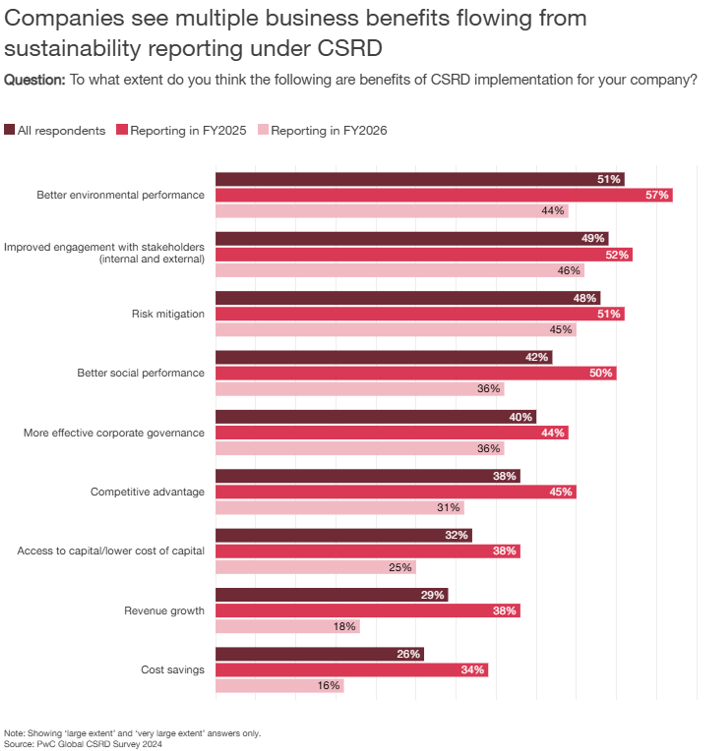
The survey also underscores sustainability reporting as a competitive differentiator and governance enhancer. To comply with CSRD and achieve sustainability targets, businesses are leveraging e-invoicing to automate data capture, enhance transparency, and streamline compliance across complex supply chains.
Together, these findings demonstrate that beyond cost and efficiency gains, sustainability imperatives are increasingly driving the global shift toward e-invoicing.
Regulatory Mandates Fuelling Adoption
Governments worldwide are enforcing e-invoicing through regulatory frameworks, significantly driving adoption. Deloitte predicts that by 2030, e-invoicing will be the global standard, with tax authorities increasingly requiring real-time reporting. This shift towards digitally readable invoices clarifies tax calculations and reduces the VAT gap.
In the EU, the VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) package, adopted in March 2025, allows Member States to mandate e-invoicing from April 2025. By July 2030, all intra-EU B2B and B2G transactions will need structured e-invoices, broadening compliance.
Regional transformations are also occurring. Germany mandated structured B2B e-invoicing, compliant with EN 16931, starting January 2025. Developments tracked by EY show that countries like Italy, France, Spain, Poland, and Belgium are expanding e-invoicing mandates between 2025 and 2026.
This regulatory shift redefines compliance. Businesses must now adopt e-invoicing or face penalties. As structured invoices become mandatory, companies are integrating e-invoicing to ensure tax accuracy and maintain smooth cross-border trade.
E-Invoicing Timelines Globally
More than 100 countries now have some form of e-invoicing or continuous transaction control (CTC) requirements in place for B2B or B2G transactions. These systems often integrate with business accounting software, allowing tax authorities near real-time access to transaction data for VAT compliance and audits.
Most governments have followed a phased approach, introducing mandates in stages based on company size, industry, or invoice volume. Italy, a European pioneer, mandates e-invoicing via the FatturaPA system and has gradually expanded its frameworks to include smaller businesses and additional compliance requirements. Germany has required businesses to accept e-invoices since January 2025, with sending requirements set for 2027. Spain plans mandatory B2B e-invoicing by 2027, and France will require large and medium businesses to receive e-invoices by September 2026. Portugal continues to refine its real-time CTC system.
Conversely, the UK and Ireland lack formal mandates but are evaluating e-invoicing benefits through pilot programs to enhance market efficiency and compliance.
Recent and forthcoming key developments in e-invoicing across various regions include:
| Country | Status | Mandate Date / Details |
|---|---|---|
| Italy | Fully mandated | All B2B/B2G e-invoices via SdI in FatturaPA (XML) format since 2019. |
| Portugal | Real-time CTC and invoice validation | SAF-T, QR codes, and ATCUD codes in force since early 2020s. |
| Greece | Mandatory reporting via myDATA | VAT reporting mandatory via myDATA platform since 2020; structured e-invoicing encouraged. |
| Romania | Mandated B2B e-invoicing | SAF-T mandatory since 2022; phased B2B e-invoicing rollout. |
| Slovakia | Mandated B2G e-invoicing | B2G e-invoicing mandatory since 2023. |
| Croatia | Mandated real-time reporting | Real-time invoice reporting mandatory since 2023. |
| Germany | Receiving mandated; sending phased | Receiving mandatory from Jan 2025; sending mandate starts in 2027. |
| Poland | Mandated for large companies | B2B e-invoicing mandatory for companies with sales > €46M from Feb 2026; broader rollout to follow. |
| Belgium | Mandated B2B e-invoicing | Mandated B2B e-invoicing starting in 2026. |
| France | Receiving mandatory (large/medium) | Receiving mandatory from Sept 2026; full issuance mandate expected thereafter. |
| Spain | Mandate in development | Expected in 2027; technical specifications still under development. |
| Finland | Not mandatory, but widely used | Voluntary adoption of TEAPPS, Finvoice, Peppol BIS Billing 3.0 formats widespread. |
| Ireland | No mandate, evaluation ongoing | No B2B mandate yet; authorities evaluating frameworks. |
| UK | No mandate, evaluation ongoing | No B2B mandate yet; authorities evaluating frameworks. |
| Netherlands | No mandate, Peppol used in B2G | No B2B mandate; Peppol used voluntarily in public sector. |
| Sweden | No mandate, exploring options | No B2B mandate yet; exploring e-invoicing options. |
| Singapore | Voluntary, incentivized | Peppol adoption via InvoiceNow platform, supported by government incentives. |
| Australia | No mandate yet, phased adoption expected | Peppol adopted in public sector; roadmap for larger B2B mandates underway. |
| Malaysia | Phased implementation | Phase 1: Aug 2024 (RM100M+); Phase 2: Jan 2025 (RM25M–100M); Phase 3: Jul 2025 (RM500K+); Full rollout by Jan 2026. |
| Israel | Voluntary adoption | E-invoicing introduced gradually from 2022; full mandate expected in the medium term. |
| Latvia | Piloting and voluntary programs | Piloting and voluntary e-invoicing programs in place; mandate discussions ongoing but no full mandate yet. |
| Thailand | No mandate yet | No e-invoicing mandate yet; VAT e-reporting and digital tax initiatives progressing. |
| Ukraine | Voluntary adoption | E-invoicing introduced voluntarily with growing adoption; full mandate expected in the medium term but delayed by political and economic challenges. |
E-Invoicing and CTC Mandates by Year
2019
- Italy: Initiates full mandatory B2B/B2G e-invoicing via the SdI system using the FatturaPA (XML) format.
2020
- Greece: Introduces mandatory VAT reporting through the myDATA platform and encourages structured e-invoicing.
- Portugal: Implements real-time CTC with SAF-T, including QR codes and ATCUD codes.
2022
- Romania: Begins phased B2B e-invoicing rollout with SAF-T mandatory for large taxpayers.
- Israel: Starts gradual e-invoicing adoption with a full mandate anticipated in the medium term.
2023
- Slovakia: Enforces mandatory B2G e-invoicing.
- Croatia: Requires real-time invoice reporting.
2024
- Malaysia:
- August: Phase 1 of mandatory e-invoicing begins for companies with turnover exceeding RM100 million.
2025
- Germany:
- January: Businesses must receive e-invoices in XRechnung/ZUGFeRD formats.
- Malaysia:
- January: Phase 2 of mandatory e-invoicing extends to businesses with turnover between RM25M and RM100M.
- July: Phase 3 extends the mandate to businesses with turnover exceeding RM500K.
2026
- Malaysia: Full nationwide mandatory e-invoicing rollout by January.
- Poland:
- February: Mandatory B2B e-invoicing for companies with sales > €46M begins; broader rollout to follow.
- Belgium: Initiates mandatory B2B e-invoicing requirement.
- France:
- September: Mandates large/medium enterprises to receive e-invoices in Factur-X or Peppol BIS 3.0 formats, with full issuance mandate post-2026.
2027
- Germany: Begins phased mandate requiring businesses to send e-invoices.
- Spain: Expected to mandate B2B e-invoicing; technical specs under development.
Ongoing / No Mandate Yet / Voluntary Adoption
- Finland: B2B e-invoicing is voluntary but widely used in formats like TEAPPS, Finvoice, and Peppol BIS Billing 3.0.
- Ireland, UK, Netherlands, and Sweden: No B2B mandates currently, but active evaluations and pilot programs are in place. Peppol is used voluntarily in some sectors.
- Singapore: No mandate, but strong government incentives encourage Peppol-based e-invoicing.
- Australia: No mandate yet, but Peppol adoption is growing, especially in the public sector, with a government plan for a progressive rollout.
- Latvia: Engaged in piloting and voluntary programs with mandate discussions ongoing.
- Thailand: No mandate, but VAT e-reporting and digital tax initiatives are progressing.
- Ukraine: Adopts e-invoicing voluntarily, with a full mandate delayed due to challenges.
The worldwide shift toward electronic invoicing is happening quickly as countries enforce various mandates for compliance, efficiency, and digital transformation. Some regions are leading, while others pilot the technology, underscoring the global shift toward digitized financial processes. With more countries on board, businesses must stay informed and adapt to maintain a competitive edge and operational fluidity. Understanding these developments is crucial for navigating international trade and taxation complexities.
E-Invoicing in the U.S.
E-invoicing adoption in the U.S. has historically lagged behind regions like Europe and Latin America, mainly due to the lack of a federal mandate and the decentralized nature of U.S. tax administration. However, 2025 marks a significant shift with rapid adoption driven by the pursuit of efficiency gains and a stronger integration into global digital trade networks. Here are some key developments:
- Business Payments Coalition Initiative:
- In collaboration with the Federal Reserve, the BPC is piloting a nationwide e-invoicing exchange framework.
- This aims to establish an interoperable, standardized model, likely utilizing Peppol protocols, for secure and efficient exchange of e-invoices among U.S. businesses.
- The pilot involves ERP vendors, payment processors, and corporate participants in an active voluntary network.
- Efficiency and Cost Savings:
- U.S. businesses are acknowledging the benefits of e-invoicing for streamlining accounts payable/receivable, reducing manual processing errors, and enhancing cash flow.
- Global Compliance Pressures:
- As major trade partners like the EU, India, and China enforce mandatory e-invoicing frameworks, U.S. exporters and importers are updating systems to remain competitive and compliant.
- Fraud Prevention and Audit Readiness:
- Structured, digital invoicing helps reduce the risk of invoice fraud, duplicate payments, and disputes while improving audit trails.
Although there is no national e-invoicing mandate yet, the shift towards adoption is clear. Analysts predict that, within the next few years, industry-led frameworks will reach critical mass, making voluntary adoption commonplace for larger enterprises and their trading partners, particularly in sectors like healthcare, transportation, and public procurement.
The U.S. stands at a strategic crossroads: with maturing infrastructure pilots and expanding commercial use cases, e-invoicing is transitioning from an “optional innovation” to a strategic necessity for U.S. businesses aiming for global operations and digital efficiency at scale.
The Benefits of E-Invoicing
E-invoicing offers a wide range of benefits that enhance business operations in various ways. By implementing this digital solution, businesses can achieve substantial cost savings, boost compliance and accuracy, streamline operations through automation, support sustainability initiatives, and reinforce vendor partnerships. These advantages are crucial for organizations seeking to improve financial processes, increase efficiency, and stay competitive in an ever-changing marketplace.
1. Cost Efficiency and Accelerated Cash Flow
E-invoicing offers a pathway to substantial cost savings by:
- Eliminating expenses related to printing, postage, and manual handling of paper invoices.
- Accelerating the invoicing process, resulting in faster payments and improved cash flow management.
- Minimizing errors and discrepancies, thereby reducing the likelihood of costly disputes and penalties.
- Allowing reallocation of savings to strategic initiatives that drive growth and innovation.
2. Enhanced Accuracy and Error Reduction
The precision of e-invoicing helps maintain financial integrity by:
- Reducing manual errors through automated invoice processing.
- Ensuring compliance with tax regulations and meeting financial reporting requirements.
- Supporting better decision-making with accurate data, enabling businesses to optimize their operations and strategies.
3. Streamlined Operations Through Automation
Efficiency improvements with e-invoicing are realized by:
- Automating the procure-to-pay process to reduce time and resources spent on manual tasks like data entry and approval workflows.
- Leading to quicker invoice approvals and payments, thereby improving vendor relationships and securing favorable terms.
- Freeing up employee time for strategic initiatives and value-added activities.
4. Advancing Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
E-invoicing aligns with sustainability goals through:
- Reducing paper usage and waste, significantly decreasing environmental impact.
- Enhancing a company’s reputation and brand image by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability.
- Contributing to a more sustainable business model and future.
5. Strengthening Vendor Partnerships Through Enhanced Communication
E-invoicing improves relationships with vendors by:
- Providing real-time access to invoice data, facilitating more effective collaboration.
- Reducing disputes and fostering trust through improved communication and transparency.
- Leading to stronger partnerships and securing more favorable terms and conditions, enhancing operational efficiency and competitiveness.
Getting Started with E-Invoicing
Transitioning to e-invoicing requires careful planning and execution. Here are some steps to help businesses get started:
- Assess Current Processes: Evaluate existing invoicing workflows to identify areas for improvement and automation.
- Select an E-Invoicing Solution: Choose a platform that meets your business needs, considering factors like compatibility, scalability, and security. SoftCo’s e-invoicing solution is a reliable option.
- Ensure Compliance: Stay informed about relevant regulations and ensure your e-invoicing practices align with them.
- Train Staff: Educate your team on the new system and processes to ensure a smooth transition.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously evaluate the e-invoicing system’s performance and make necessary adjustments to optimize efficiency.
By following these steps, businesses can successfully implement e-invoicing and reap its numerous benefits.