The manufacturing industry is at a crossroads. With a growing labor shortage and a widening skills gap, businesses are struggling to find and retain qualified workers. A Deloitte report warns that by 2033, nearly 1.9 million manufacturing jobs could go unfilled due to a lack of skilled talent.
But rather than replacing workers, automation is redefining the workforce—streamlining operations, enhancing productivity, and opening new career opportunities. Advanced robotics, AI, and smart manufacturing technologies are shifting the focus from manual labor to highly skilled, technology-driven roles.
In this blog, we’ll explore:
- The biggest workforce challenges in manufacturing today.
- How automation is bridging the skills gap and reducing labor shortages.
- Why upskilling is critical for the next-gen manufacturing workforce.
- The future of human-machine collaboration and what it means for industry growth.
Manufacturers who embrace automation aren’t just surviving—they’re building a smarter, more resilient workforce poised for long-term success. Let’s dive in.
The Top Workforce Challenges in Manufacturing
Impact of an Aging Workforce
The manufacturing sector is experiencing a profound impact due to an aging workforce. As seasoned employees retire, the industry faces a significant loss of expertise and institutional knowledge. This trend exacerbates the manufacturing labor shortage and widens the skills gap. According to Deloitte, U.S. manufacturing employment has actually surpassed pre-pandemic levels, standing close to 13 million.
Yet the need for skilled workers continues to rise. An aging workforce means that fewer young workers are available to fill these crucial roles. Bain & Company reports that globally, 150 million jobs will shift to workers 55 and older by 2030 and, on average, will account for over 25% of the workforce across the U.S., Japan, and Europe—a trend that has developed over the past 20 years.
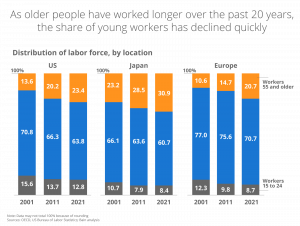
This demographic shift leads to a shortage of potential candidates, further straining the talent pool. This scenario is creating several challenges for the industry, that include:
Top 6 Challenges of an Aging Workforce in the Manufacturing Industry
- Erosion of Expertise: Retirements lead to a loss of critical expertise and specialized skills vital for maintaining efficient workflows and production standards.
- Escalated Training Investments: Replacing retiring workers with less-experienced talent requires extensive training, increased spending on skill development and onboarding.
- Diminished Adaptive Capacity: The departure of experienced workers reduces agility in adopting new technologies, hindering swift responses to market demands.
- Increased Operational Costs: Retired employees shift healthcare and benefits costs, impacting operational expenses and requiring careful management for cost-effectiveness.
- Promotion Stagnation: Delayed retirements hinder turnover, limiting career progression for younger employees and affecting motivation and development.
- Ineffective Knowledge Transfer: Without structured mentorship, transferring valuable knowledge is challenging, risking the loss of institutional memory needed for operations continuity.
Strategic workforce planning is essential for manufacturers to mitigate these impacts and ensure a resilient, competitive industry.
Talent Deficit in Manufacturing
Manufacturing faces a critical talent deficit, impacting its growth and innovation potential. According to a report by EY, 74% of manufacturing leaders say that the skills needed for manufacturing jobs are changing rapidly while 65% also strongly believe that the skills needed for changing manufacturing jobs are outpacing the current workforce, thus creating a persistent skills gap.
This shortage is not merely a lack of skilled workers but also a gap in applicants for open positions. As industry growth accelerates, the need for diversified skills, including technical, digital, and soft skills, becomes essential. The shortage affects entry-level positions up to highly skilled engineering roles, leaving manufacturers struggling to fill vacancies.
7 Ways in Which the Talent Deficit is Impacting the Manufacturing Industry:
- Stifled Innovation and Growth: A shortage of skilled workers hampers innovation, delaying crucial research and development roles, impacting new products and processes, and affecting competitiveness.
- Increased Labor Costs: With fewer skilled candidates, manufacturers offer higher wages and benefits to attract and retain talent, raising operational expenses.
- Operational Inefficiencies: The scarcity of skilled labor lengthens training periods and slows new hire integration, leading to inefficiencies and potential production delays.
- Quality Issues: Fewer experienced staff make it challenging to maintain high standards, risking defects and customer dissatisfaction, which can damage brand reputation.
- Reduced Responsiveness: Insufficient skilled personnel hinder rapid responses to market shifts, product customization, or scaling operations, affecting market position.
- Workforce Strain: The talent gap increases workloads on current employees, risking burnout and potentially raising turnover rates.
- Delayed Technology Adoption: A skilled workforce shortage slows the implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies, crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
To mitigate these impacts, manufacturers must invest in strategic talent acquisition and retention strategies, expand recruitment efforts to non-traditional talent pools, and prioritize workforce development and upskilling initiatives. This proactive approach is essential to ensuring the industry can attract and retain the necessary workforce to sustain the long-term resilience and competitiveness of the manufacturing industry.
How Automation Bridges the Skills Gap in Manufacturing
Automation’s Role in Reducing Manual Labor and Enhancing Productivity
Automation plays a crucial role in minimizing reliance on manual labor and increasing productivity in manufacturing. By integrating advanced technologies such as robotics and artificial intelligence, manufacturers can streamline operations with automated systems that undertake repetitive and laborious tasks.
This is a new approach for the manufacturing sector, according to McKinsey, where automation has historically been used to improve quality or to address health and safety issues. They report that the price of robotic automation continues to fall compared with labor costs, making the ROI increasingly more attractive.
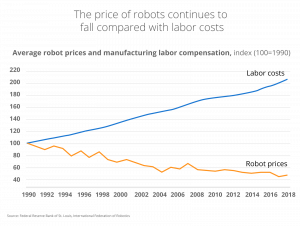
The transition to automation allows human workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities, thus addressing labor shortages and improving overall efficiency.
5 Ways to Reduce Manual Labor and Enhance Productivity with Automation:
- Task Automation: Automating repetitive tasks enables employees to engage in strategic and creative roles that require human skills, allowing machinery to operate without breaks and surpass human limitations.
- Error Reduction: Consistent machine operation reduces errors, enhances safety, reduces defects and returns, boosts customer satisfaction, and maintains quality reputation.
- Real-time Monitoring: Advanced technology allows for immediate production adjustments, enabling manufacturers to swiftly address issues and adapt to demand changes using continuous optimization with sensors and data analytics.
- Continuous Production: Automation ensures uninterrupted production, eliminating human fatigue and shift-related pauses, thereby boosting capacity and job stability.
- Predictive Insights: AI and machine learning provide foresight into potential issues, enhancing resource optimization, decision-making, and supporting innovation and process improvement.
Automation significantly reduces reliance on manual labor by assuming repetitive tasks, boosting manufacturing efficiency. This transition enhances productivity, enabling human workers to engage in strategic, innovative roles. Consequently, it underscores the necessity of upskilling the workforce to manage and optimize these advanced systems, fostering agility and resilience in adapting to technological advancements.
Upskilling the Workforce Through Manufacturing Automation
Upskilling for Automation in Manufacturing
As automation becomes integral in manufacturing, training employees for system management is crucial for optimal operations and maximizing technological investments. Upskilling should cover both technical abilities, like operating, troubleshooting, and programming automated equipment, and soft skills such as problem-solving, adaptability, and communication. According to Forbes, preparing employees to work with automation can be achieved with the following strategies:
- Education and Training Programs
- Collaborative Work Environments
- Clear Communication and Expectations
- Empowering Creativity and Innovation
- Ongoing Feedback and Support
Investing in upskilling addresses the skills gap while enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Top 5 Benefits of Upskilling the Workforce for Automation
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Targeted training enables employees to effectively manage and optimize automated systems, decreasing downtime and enhancing productivity in manufacturing.
- Improved Innovation: Continuous learning empowers workers to improve processes and develop new products, strengthening the company’s competitive edge.
- Increased Job Satisfaction: Upskilling broadens employee career opportunities and fosters a sense of achievement, enhancing satisfaction.
- Higher Retention Rates: Investing in employee development creates a supportive environment, encouraging loyalty and reducing turnover costs.
- Agility and Resilience: A learning-driven workforce is better prepared to adapt to technological changes and market shifts, maintaining industry competitiveness.
Collaborating with Automated Machines in Manufacturing
Automation is no longer just about replacing manual labor—it’s about creating a powerful partnership between humans and machines. As technology advances, automation is becoming more seamlessly integrated into manufacturing processes, allowing machines to handle repetitive, precision-driven tasks while workers focus on problem-solving, innovation, and strategic decision-making.
For manufacturers, the key challenge is not just adopting automation but ensuring it enhances human capabilities rather than replacing them. This means designing workflows where technology and people work in harmony to drive efficiency, quality, and productivity.
This transformation is already underway, but there’s still progress to be made. According to The Manufacturing Leadership Council, 50% of manufacturers believe their factories will be “getting smarter but still a work in progress” by 2026. To stay ahead, companies must invest in training, rethink traditional job roles, and build a workforce that can adapt to an increasingly automated environment.
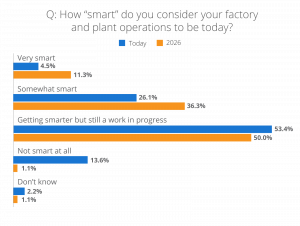
A recent article by Forbes quotes the International Federation of Robotics and their report that collaboration between machines and manufacturing employees is projected to increase productivity by up to 30%, cut labor costs significantly, and improve workplace safety with fewer accidents. Implementing new workflows and investing in training are crucial to maximizing this collaboration, paving the way for a more innovative and resilient manufacturing sector.
7 Benefits of Collaborative Human & Machine Workflows in Manufacturing
- Increased Efficiency: Automating repetitive tasks allows human workers to focus on complex, strategic activities, boosting operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Quality Control: Automation ensures consistent output with minimal errors, strengthening quality control and reducing defects.
- Reduced Downtime: Machines operate continuously without fatigue and can be quickly adjusted with human oversight to minimize downtime.
- Cost Savings: Efficient use of resources and labor through automation lowers operational costs while maintaining or enhancing output.
- Improved Safety: Machines handle hazardous tasks, lowering workplace injury risks and creating a safer environment for human employees.
- Faster Production Times: Integrating machines into workflows speeds up production, meeting market demands more effectively.
- Fostering Innovation: Free from routine tasks, employees can pursue creative solutions and drive new process innovations.
By understanding and leveraging these benefits, manufacturing companies can create robust, agile systems that maximize the potential of both human and machine capabilities, paving the way for a future-ready industry.
The Future of the Workforce in an Automated Manufacturing Environment
As manufacturing continues to evolve, automation is no longer just a tool for efficiency—it’s a key driver of workforce transformation. When properly integrated, automation can help build a resilient, future-ready workforce that thrives alongside machines.
According to Forbes, the most adaptable manufacturing workforces share four key traits: agility, responsiveness, flexibility, and predictability. To develop these qualities, manufacturers must take proactive steps to prepare their employees for an increasingly automated environment.
6 Steps to Build a Future-Ready Manufacturing Workforce
- Prioritize Continuous Learning & Development
Invest in training programs that help employees reskill and upskill, ensuring they can effectively manage and optimize new technologies. - Develop Both Technical & Soft Skills
Focus on technical expertise—such as data analysis and machine monitoring—while also strengthening soft skills like communication and adaptability. - Encourage an Innovative Mindset
Foster a culture where employees feel empowered to explore new ideas, experiment with automation-driven processes, and drive manufacturing advancements. - Strengthen Human-Machine Collaboration
Create workflows that leverage the strengths of both people and machines, improving productivity, efficiency, and innovation across operations. - Adopt Adaptive Workforce Strategies
Build flexibility into workforce planning so teams can quickly adjust to technological changes and market demands, ensuring long-term competitiveness. - Enhance Employee Engagement & Retention
Establish clear career pathways that help employees see growth opportunities in an automated environment, increasing job satisfaction and retention.
The Smart Factories of the Future
Looking ahead, manufacturing will be dominated by smart factories powered by IoT, AI, and robotics. These technologies will enable real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance, and fully connected production lines.
As a result, the workforce will shift from manual, repetitive roles to more technical, strategic, and problem-solving positions. Key responsibilities will include:
- System Management – Overseeing automated workflows
- Process Optimization – Improving efficiency with data-driven decisions
- Troubleshooting & Maintenance – Ensuring seamless machine performance
- Strategic Planning – Aligning technology with business goals
Final Thoughts
Automation isn’t replacing workers—it’s redefining their roles. With the right training and workforce strategies, manufacturers can close the skills gap, boost productivity, and stay competitive. The future of manufacturing is about people and technology working together to build smarter, stronger industries.


